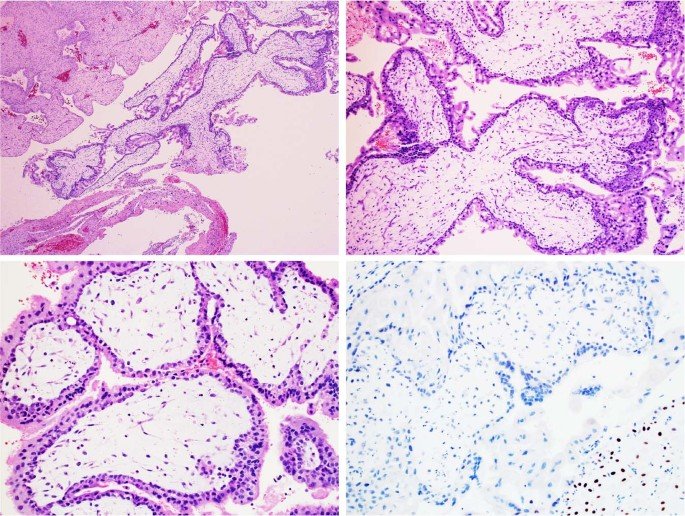
what is Choriocarcinoma/gestational trophoblastic neoplasia?
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is the term given to a group of rare tumors that develop during the early stages of pregnancy. After conception, a woman’s body prepares for pregnancy by surrounding the newly fertilized egg or embryo with a layer of cells called the trophoblast. The trophoblast helps the embryo implant itself to the uterine wall. These cells also form a large part of the tissue that make up the placenta — the organ that supplies nutrients to a developing fetus. In GTD, there are abnormal changes in the trophoblast cells that cause tumors to develop.
Types of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia:
Choriocarcinoma: This cancerous tumor forms inside a pregnant woman’s uterus. Choriocarcinomas usually occur when growths from molar pregnancies turn cancerous. Rarely, choriocarcinomas form from tissue left in the uterus after a miscarriage, an abortion or the delivery of a healthy baby.
Invasive mole: Trophoblast cells form an abnormal mass that grows into the muscle layer of the uterus.
Placental-site trophoblastic tumor: This extremely rare, slow-growing tumor develops where the placenta attaches to the uterine wall. Placental-site trophoblastic tumors are often not discovered until years after a full-term pregnancy.
Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor: This extremely rare tumor’s progression mimics that of a placental-site trophoblastic tumor.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Symptoms:
• Bleeding or discharge not related to your periods
(menstruation)
• A larger-than-usual uterus while pregnant
• Pain and/or mass in the pelvic area
• Extreme bouts of nausea and vomiting
The symptoms listed above are also associated with many other gynecologic and pregnancy-related conditions. However, the only way to know if your symptoms are being caused by GTD is to have them evaluated by a doctor.